With a growing emphasis on environmental consciousness and sustainability, the manufacturing sector finds itself at a significant crossroads. The well-established linear production models, involving resource extraction, utilisation, and disposal, have become increasingly unsustainable. In response to this pressing need for change, manufacturers are embarking on a transformative journey. They are shifting their focus towards the principles of the circular economy and actively investing in recycling initiatives. This blog embarks on an exploration to understand how the circular economy and recycling practices are shaping the landscape of the manufacturing industry, with the promise of a sustainable future for future generations.
The Circular Economy: A Paradigm Shift
At its core, the circular economy is a holistic approach to resource management. Unlike the linear economy, which follows the “take-make-waste” model, the circular economy focuses on extending the life cycle of products, materials, and resources. It aims to minimise waste, reduce the depletion of natural resources, and maximise the value extracted from existing materials.
Key Principles of the Circular Economy in Manufacturing
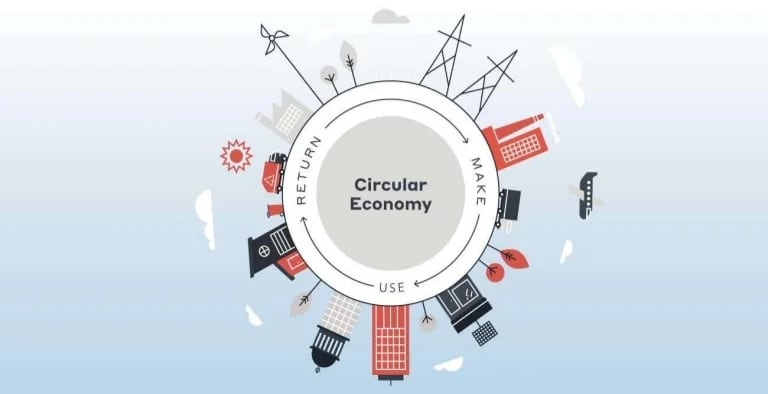
Design for Sustainability:
Manufacturing companies are increasingly emphasising product design that promotes longevity, reparability, and recyclability. This involves the use of durable materials and components that can be easily disassembled and reused.
Extending Product Life:
Manufacturers are exploring strategies to prolong the useful life of their products. This includes offering repair services, facilitating upgrades, and supporting the resale of used items.
Reuse and Remanufacturing:
The concept of reusing components and parts in remanufacturing processes is gaining momentum. By refurbishing and restoring used products to like-new condition, manufacturers reduce the demand for new resources.
Material Efficiency:
Companies are optimising material usage by minimising waste and exploring alternatives to traditional materials. This includes using recycled or upcycled materials whenever possible.
Recycling Initiatives in Manufacturing
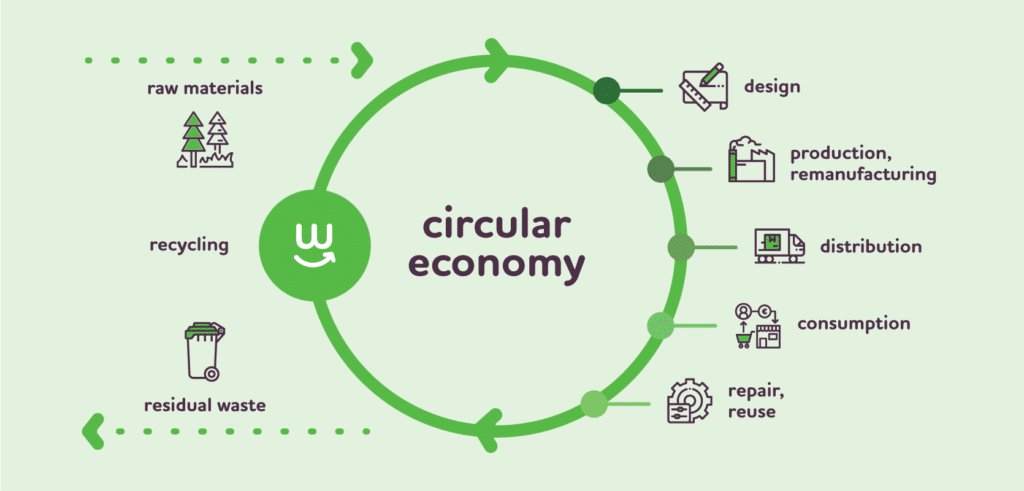
Recycling plays a pivotal role in the circular economy. In the manufacturing sector, recycling efforts are multifaceted, encompassing both internal and external processes. Manufacturers are making significant strides in several areas. Microsoft D365 plays a pivotal role in enabling these recycling efforts:
Internal Material Recycling with D365:
Manufacturers use D365 to manage the recycling and reuse of their production waste. D365 offers essential tools for efficient material tracking and management, ensuring that scrap metals, plastic waste, and other byproducts are recycled to minimise waste and reduce the need for new materials.
Supplier Collaboration via D365:
Collaborating with suppliers to source recycled materials or products made from recycled content is made more accessible with D365. This collaborative platform helps manufacturers close the loop in their supply chain, promoting sustainable sourcing practices.
End-of-Life Product Recycling with D365:
D365 is increasingly being used to manage the recycling of products at the end of their life cycle. It facilitates the design of products with recyclability in mind and establishes systems for the efficient collection and recycling of old products.
Consumer Engagement Supported by D365:
D365 also plays a critical role in raising awareness and encouraging consumers to recycle products. Manufacturers employ D365 to educate consumers about the importance of recycling and provide convenient methods for recycling their products.
Real-World Examples of Circular Economy Success

Interface, Inc.:
The global modular flooring manufacturer, Interface, has set a goal to become carbon negative by 2040. They are pioneering the use of recycled and bio-based materials in their products, emphasising product design for disassembly, and promoting their “Take Back” program, which reclaims and recycles old carpet tiles.
H&M:
The fashion industry is embracing circular economy principles, and H&M is a notable example. They offer an in-store clothing collection program, encouraging customers to recycle old clothing in exchange for store vouchers. H&M also produces clothing with sustainable materials, emphasising recycling and repurposing textiles.
Challenges and Obstacles
While the circular economy and recycling offer numerous benefits, there are challenges manufacturers must overcome:
Lack of Standardisation:
Establishing standardised recycling processes and material specifications can be a hurdle, especially for materials not commonly recycled in the past.
Consumer Behavior:
Encouraging consumers to recycle and opt for sustainable products can be challenging. Manufacturers must invest in education and marketing efforts.
Investment Costs:
Transitioning to circular economy practices may require substantial upfront investment in technology and process optimisation.
Government Regulations and Incentives
Government regulations and incentives can play a crucial role in promoting the circular economy and recycling. Many governments worldwide are introducing policies to encourage sustainable practices, including extended producer responsibility (EPR) regulations, tax incentives for recycling initiatives, and mandatory recycling targets.
Conclusion
The transition to a circular economy and a strong emphasis on recycling are not just buzzwords; they are essential steps towards ensuring a sustainable future. The manufacturing industry is embracing these principles with enthusiasm, redefining production processes, product design, and material usage to minimise waste and maximise resource efficiency.
As we look ahead, manufacturers are poised to lead the charge in reimagining how we produce, consume, and manage resources. The circular economy and recycling in manufacturing are not just environmental goals; they are economic imperatives that will drive innovation, reduce environmental impact, and create a more sustainable and prosperous world for all. The journey has begun, and the future is circular.




